FPS, frames per second, or framerate all mean the same thing. Don’t confuse FPS with first-person shooter, which is a genre of games (such as Counter-Strike). The in-game FPS you will get is more or less determined by the hardware you have, what game you’re running, and what settings you’re playing the game in. Still, there are a few important considerations to remember for a potentially better gaming experience.
Will Upgrading Graphics Card Improve FPS?
Yes. The graphics card is the most important piece of hardware in a gaming PC vs. CPU, RAM, or anything else. Buying a more powerful GPU will always lead to higher FPS, unless if the game is badly optimized for the GPU in question or your drivers aren’t working. Every new generation of GPUs can see anywhere from a 10 to 40% jump in performance within the same price range. Upgrading any other component, such as the processor, RAM, SSD, or power supply will not have as big of an impact as buying a more powerful, faster graphics card in terms of gaming FPS.
Should I Cap My FPS at the Refresh Rate?
Yes. Your GPU might be able to render a game at 200 FPS, but if your monitor’s refresh rate is 144 Hz, then it means that it cannot display anything over 144 images in a second. The refresh rate is the maximum FPS your monitor can show, even if the GPU is rendering more frames. That’s why it’s always recommended to cap your FPS at your monitor’s refresh rate to avoid wasting performance (and therefore, power) on frames that won’t see the light of day anyway. Learn more here.
How to Boost FPS
There are a few ways to go about it.
Sacrificing Quality
The most reliable way to increase FPS is to sacrifice the quality of the game. This includes lowering the in-game graphics quality, setting a maximum FPS, or reducing the window resolution. All of these will offer noticeable improvements.
Without Sacrificing Quality
Enable Windows Game Mode, update drivers, remove background programs, disable unnecessary background services, and double-check the refresh rate of your monitor to sync it with your GPU. If you’re on a laptop, always game when plugged in, and make sure the power mode is set to High Performance (when plugged in). At best, expect marginal improvements. At worst, these steps won’t do anything.
Overclocking
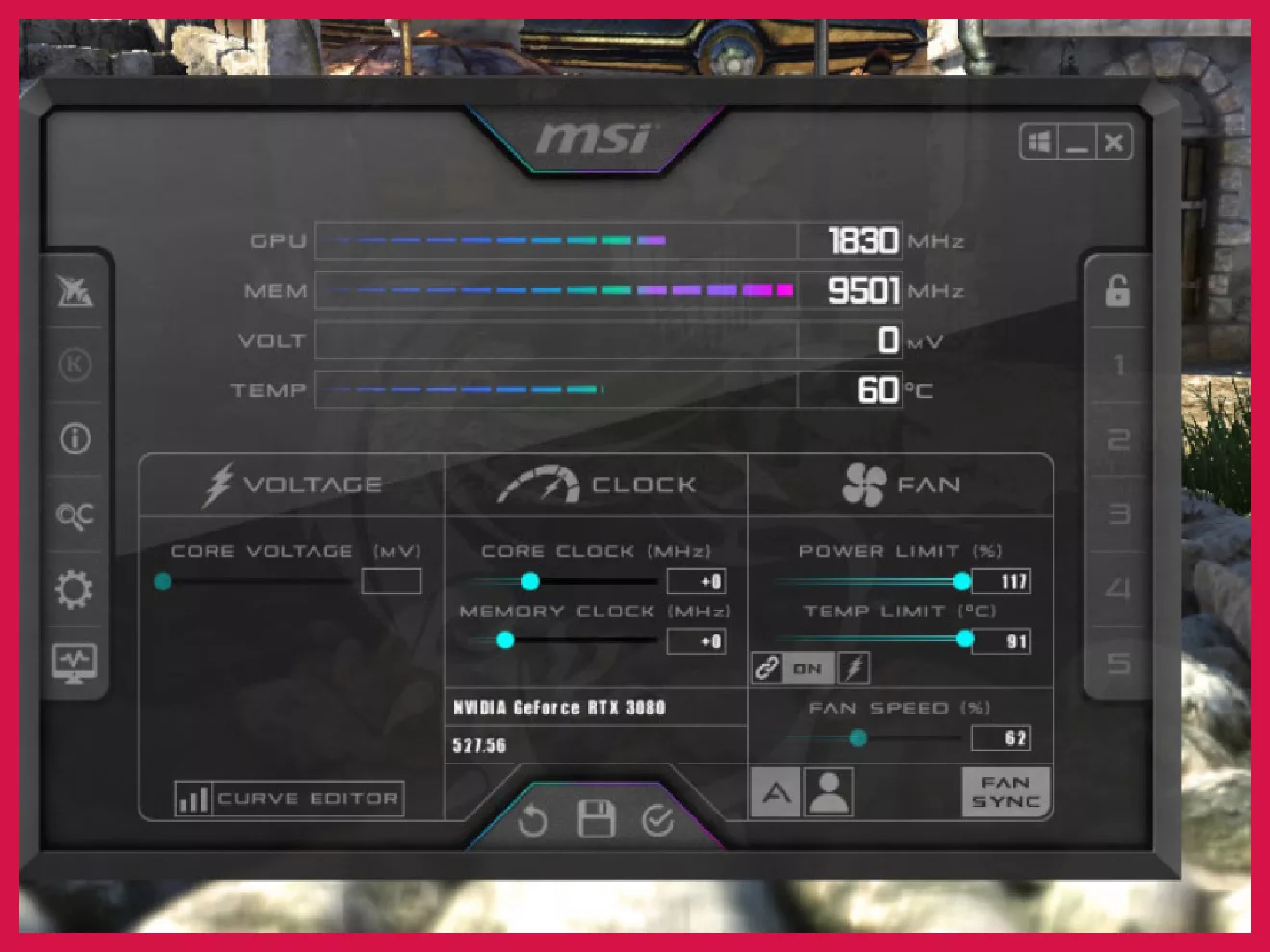
Another excellent method of increasing FPS is overclocking. It causes no quality sacrifice and the results are remarkable. Overclocking should only be done if you know what you’re doing. Note that it voids your GPU’s warranty (though nobody can possibly know if you’ve overclocked your GPU). Any modern graphics card is built with enough safe headroom to self-overclock when demanded. Tools like MSI Afterburner or AMD Software’s overclocking feature just take it one step further. Increment your clock speed and power draw in small steps until you get a crash. Once you’ve found a stable overclock, run the overclocking software before playing games. Read our guide on overclocking.
Upscaling
Another fairly new trick of the trade is to use upscaling technologies. These technologies lower the display resolution of the game. As I said earlier, lowering the resolution can have a significant impact on your FPS, but it makes the image look choppy and lower quality, of course. Think reducing the resolution of a YouTube video from 1080p to 720p. These tools downscale the image resolution and then use intelligent optimizations such as sharpening to offer a good-looking image. The result is a huge boost in FPS without losing quality at all. There are three such tools:
- Nvidia’s DLSS is the best one so far in terms of performance and quality. It only works with Nvidia’s cards that have specialized AI cores for this, so that means RTX series and up. GTX cards can’t use this.
- AMD’s FSR is hardware-agnostic and instead takes the software route. It’s not as good as Nvidia DLSS, but it can be used by any GPU. This includes old, new, Nvidia, AMD, and integrated graphics as well.
- Intel’s answer to DLSS and FSR is its XeSS technology that works on Intel’s own GPUs such as the Arc series. If you have one, you might want to try it out.
Check officially supported games here – DLSS | FSR 1, 2, and 3 | XeSS (reportedly the list is longer).
Troubleshooting: Why is My FPS So Low?
If you’re doing everything right and still getting low FPS, it could be an issue with some other component. Here are some common culprits:
- CPU Bottleneck: All data needs to go through the processor. If your processor is limiting your GPU, it’s called a CPU bottleneck and it’s extremely easy to test. In your Task Manager, check if CPU usage is 90% or higher while the GPU performance is comfortably lower. If yes, this is a CPU bottleneck case and you need to upgrade it. Learn how to check if your CPU is bottlenecking your GPU in more detail.
- Thermal Throttling: If you experience comfortable FPS for a while and then sudden dips when the game becomes 50-60% slower, jarring, and low FPS, then it’s a classic case of thermal throttling. Your GPU is not getting cooled fast enough. Look for case airflow problems and think of getting new fans. Here are five time-tested tips to better manage GPU temperature.
- Bad Optimization: If you’re getting low FPS in a particular game, then it could just be a matter of bad optimization. For example, the RTX 3060 Ti has a notorious reputation for low FPS in many popular games like Warzone, and how you troubleshoot that is going to be very different from, let’s say, an RTX 4090 performing badly in a different game.
Other components can also cause issues but those are more serious than low FPS. For example, insufficient RAM can lead to system freezes, older HDDs can cause extremely slow game loading, and a faulty PSU can cause crashes when you launch a game.
What Factors Influence FPS?
The factors that influence FPS the most include the GPU (most important) and the CPU. After that, other hardware components also play instrumental roles. The monitor’s refresh rate is the maximum FPS you will see (though the reported FPS isn’t influenced). A processor that cannot catch up and bad cooling also influences FPS. Bad drivers, poor optimization, or buggy updates can also cause low FPS.
How to Increase FPS to 120, 144, or 240?
First, you need to get a monitor with a refresh rate of 120 Hz, 144 Hz, or 240 Hz. After that, you need to do some research to find the right GPU that can accomplish the desired FPS in the game you’re about to play. Here are some common cases, for example:
- GTX 1660 Ti can do 170 FPS in GTA V at ultra settings.
- GTX 1060 3GB can only manage 50-55 FPS even at low settings in Warzone 2.
- RTX 2060 6GB can barely cross 25 FPS in Cyberpunk at Ultra with ray tracing on and DLSS on.
- RX 6600 XT can manage a steady 60 FPS in Elden Ring at 1080p and maximum settings.
Every generation has premium, high-end models. Those can run the best games (AAA titles from the last 4-5 years) comfortably at 1440p, 4K, and even 8K resolution at maximum settings and with ray tracing on. Buy the right GPU for your use case to ensure 120 FPS, 144 FPS, 240 FPS, or any other FPS.
Does FPS Increase Speed in Games?
Technically, yes. The better term is “smoother” and not “faster.” In lower tiers, FPS gains are more noticeable and stunning. For example, going from a console’s 30 FPS to a gaming PC’s 60 FPS is nothing short of magic. Going from 60 to 90 FPS in the same game, however, won’t be the same significant experience. Big jumps can still be considerably smooth – so going from 60 to 150 FPS, let’s say, will be a nice improvement. Beyond a point, roughly 150-200 FPS in most games in my experience, further gains kind of become pointless. You simply cannot process the smoothness anymore, so there’s hardly anything noticeably faster. Still, in certain situations (such as competitive tactical shooter games), going 250+ FPS can offer advantages to some players. It doesn’t apply to all gamers.