It’s perfectly normal to have some type of delay between the source and the Bluetooth device. It happens due to several very practical reasons. These common issues can easily be fixed. All you need to do is read this guide and keep your patience – it might come in handy. Knowing what are the common causes and how they happen can be key to knowing how to fix sound delay in Bluetooth headphones, so that’s what we’ll start with.
What is a sound delay in Bluetooth headphones?
Knowing what classifies as a delay is the first step toward understanding how to fix sound delay in Bluetooth headphones.
When the audio is out of sync with the video, it’s a sound delay. It means that although you see what’s happening, the sound for the actions comes a bit later. This delay is caused due to a number of issues that we’ll tackle in the next section.
More technically, this is called Bluetooth audio lag and is a fairly common phenomenon with all types of Bluetooth sound devices, including your wireless headphones.
What causes a sound delay or audio lag in Bluetooth headphones?
Baby steps. The second detail that you need to acquaint yourself with is what causes the audio lag.
What, indeed.
Bluetooth is a wireless medium for audio transmission. And due to certain logical reasons, the connection can become “weak.” A weak connection will start to produce lag in the audio transmission (and in certain cases, also what you’d call “breakages”, choppiness, or stuttering).
The most common culprits behind Bluetooth audio lag are these:
- Distance: The distance between the transmitter or source and the receiver directly affects the quality of the Bluetooth connection. Every Bluetooth device has an “effective range”, beyond which it fails to send audio data in time to match the source.
- Interference: Other wireless devices (including other infrared and Bluetooth devices) can produce interference, which commonly results in noise in audio but can additionally produce sound delay as well.
- Codec difference: Bluetooth audio transmission works on codec-based compression and decompression. The data is essentially compressed using an algorithm determined by the codec in use. And as a general rule of thumb, some codecs are better than others. It’s known that certain Bluetooth codecs under certain specific conditions can make a mess of compression. Bad compression and decompression can also cause audio lag.
- Older Bluetooth technologies: Just like any other data transmission technology, Bluetooth has also grown with time. Bluetooth as technology is about 21 years old. The tenth version of Bluetooth, Bluetooth 5, came out in 2016. Each new version added the effective range and transmission speeds mainly. So, older Bluetooth versions can be very ineffective in terms of range, transmission speed, or overall reliability with modern devices.
- Source audio quality and size: The bigger and higher quality the source audio file is, the more bandwidth the audio signal requires for transmission. Due to bandwidth limitations, Bluetooth headphones might experience lag when playing files that require higher than usual bandwidth. Higher quality files such as FLAC music or bigger music files (in terms of how much storage space they use) both affect this.
Bottom line is, audio transmission over Bluetooth depends on several factors. Digital data is converted to an audio signal, streamed, received on the other end, and then reconverted back into digital data.
The transmitter is the source of the audio. It can be a PC, smartphone, or MP3 player, for example. The receiver is the device you hear the audio on. It can be a headphone or a speaker, for example.
For wireless Bluetooth headphones, the audio latency (the time it takes for the audio to travel from the transmitter to the receiver) is generally in the ballpark of 100 to 300ms.
How to fix sound delay in Bluetooth headphones: the checklist

In the previous section, we saw five potential culprits behind Bluetooth audio lag. First, you need to make sure there’s no obvious discrepancy in any one of them. If it’s a distance issue, for example, minimizing distance will fix your sound delay issue.
Let’s go over a basic checklist concerning the likely culprits before we dive deeper.
Distance
This goes without saying. If you’re experiencing lag issues only when the distance between the receiver and the transmitter is a lot, then it’s time to move to a better Bluetooth headphone or minimize the space between the two components manually.
Household items are also valid blockages that hamper Bluetooth transmission. Walls are the most prominent blockages.
If the sound starts becoming choppy or laggy as the distance increases but plays just fine when the headphones are very close to the source, then the issue is with the effective range of the transmitter (most probably) or with that of the receiver (the headphones, also less likely).
In case audio lag persists even if you’re close to the source, the problem might be something else. Move on.
Interference
The audio signal between the source and your Bluetooth headphones can be hampered by other signals. These signals include (but aren’t limited to) wifi signals from a router, television or cable signals, and other wireless devices (such as wireless mice, speakers, keyboards, printers, etc.).
Many appliances use wireless technologies. Test your headphones in a place devoid of as many wireless signals as you can possibly remove. If the problem goes away, then you know what you need to do.
Get yourself a new house with fewer appliances Use your headphones in a place that has the least amount of interference.
If interference isn’t the issue, it’s time to check your Bluetooth codecs.
Check your codecs
Some codecs are better for streaming music.
Android users have it easy. If your sound device is producing music with lag, you can change the codec on your Android device.
Note that if you’re using a Bluetooth transmitter device for your desktop PC or an inbuilt Bluetooth on a laptop, you cannot change the codec. In fact, you cannot even see what codec your Bluetooth device uses on Windows.
An external device will most likely come with its codec written on the product manual.
There are third-party apps that can help you find the codec and some excruciating methods as well that use Windows’ built-in logs system. However, these methods are generally not recommended for the lack of user-friendliness.
If you manage to find out the codec that your transmitter is using, you can find out whether or not it’s good for music streaming. If not, you can get another external Bluetooth device that has a good codec for streaming to replace the current or stock one (or supersede by disabling the stock one).
More recent Bluetooth headphones that use aptX, aptX HD, aptX LL, LC3, Sony’s LDAC, or Samsung Scalable Codec are generally far better than older devices that use the universal Bluetooth codec called SBC, which came back in 2003. If you’re looking for a new headphone, find one that uses one of these codecs.
Older Bluetooth technology
Unlike knowing the codec in use, seeing the version of the Bluetooth transmitter or receiver is much easier.
If it’s an old Bluetooth device that you’re using as a transmitter, you need to get a new one. If you’re using an old laptop, then it’s highly likely that it uses an older Bluetooth version as well, in which case I’ll recommend investing in a Bluetooth transmitter for your PC, one that’s new.
When the receiver and the transmitter aren’t using the same Bluetooth version, the connection automatically switches to the lower of the pair. For example, if your headphone uses Bluetooth 5 but the transmitter uses Bluetooth 4.1, the connection between them will be a Bluetooth 4.1 connection.
If your Bluetooth versions are new (4 or 5), then the problem might be something else. Usually, the tips above can help you debug and potentially improve your lag situation. However, if that’s not the case, we need to enter into a bit of an advanced debug mode and see what’s the fuss all about.
How to fix sound delay in Bluetooth headphones: hardware-level fixes
The fixes above were fairly basic. If they couldn’t solve your sound delay problems, then the cause is rooted in something more internal, which we’ll try to identify and fix throughout this section.
Gear up.
Optimizing a Bluetooth connection on your Windows PC
Surely, you’ve tried reconnecting the Bluetooth device or resetting the Bluetooth device itself. Updating your Windows PC and doing a restart can be the next obvious step.
If that fails to fix the issue, it’s time to check the drivers.
Bluetooth drivers
Like other types of connections, Bluetooth also works with drivers on both ends. You need to have a copy of the latest Bluetooth drivers so that the connection can be strongest.
Windows will install any appropriate drivers needed for the Bluetooth device, but it might not always update those drivers later on.
Let’s get your Bluetooth drivers updated.
- Right-click on the Start button > choose Device Manager from the list.
- Click the drop-down for Bluetooth in the left sidebar.
- All Bluetooth devices you’ve ever connected to the PC will be listed here.
- Right-click on the device you’re trying to troubleshoot (the Bluetooth headphone that’s giving you sound delay).
- Select Update Driver.
- Follow the steps to automatically install new updates and reboot your PC.
Does that solve your problem? It will work especially if you have a device that was first connected a while ago and hasn’t been updated since.
If not, let’s move on.
Windows Audio Service restart
Windows has plenty of background tasks and services that enable the operating system to, well, operate effectively.
This particular task called Windows Audio is running in the background the entire time your PC is up. Its job is to manage all the music playback.
We’ll restart this service, which is perfectly safe, to see if it solves the problem.
- Open Run (press the Windows key and R together).
- Type “services.msc” (without quotes) and hit Enter.
- The Services window will open. Scroll down to find the Windows native services. Find “Windows Audio”.
- Right-click on it and choose Properties.
- The Properties dialog box for Windows Audio will open. From the General tab, select Automatic startup type.
- Go to the Recovery tab. For First Failure and Second Failure, select “Restart the Service”. Click OK.
Do the same procedure for another service called Windows Audio Endpoint Builder. Now, disconnect your headphones, restart your PC, and reconnect your headphones once it’s on.
Troubleshooting via Windows
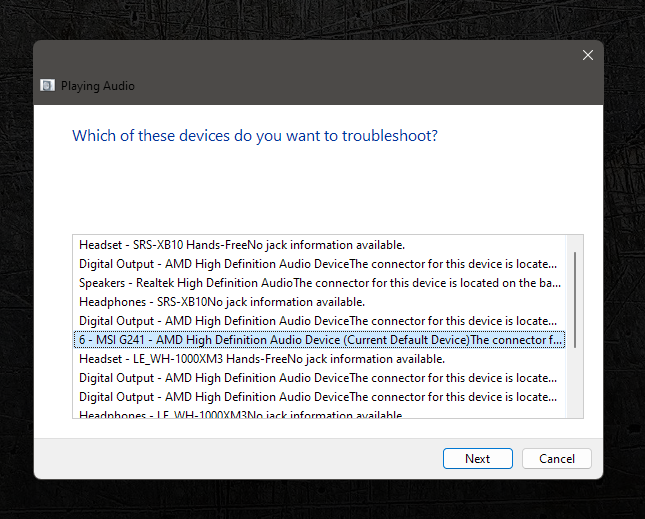
The inbuilt troubleshooter from Windows can also be useful, though not in every case.
It fixes many common problems. If yours is simply a discrepancy arising out of common issues, the troubleshooter will most probably patch it up.
Let’s see how we can troubleshoot laggy Bluetooth audio with this feature:
- Find the Speaker icon in the taskbar and right-click on it.
- From the menu that appears, select “Troubleshoot Sound Problems”.
- This will fire up a window with a list of your audio devices. Choose the device that’s experiencing problems.
- Click Next and follow the rest of the procedure as recommended by the troubleshooter.
After a bit of work, Windows will attempt to fix any issues with your device.
Wrapping up
We can’t wait for the time when Bluetooth technology is improved so much that the problem of sound delay is a thing of the past, altogether.
Bluetooth used to upgrade to a major new version every couple of years (sometimes 3). But it’s been 6 years since the latest entry on the version list: Bluetooth 5, and we’re yet to see the sixth version.
Note that different types of media can have different root causes for audio delay. For example, codecs are a major cause of music streaming lag. On the other hand, codecs don’t play a major role in the lag you experience while gaming.